Introduction to Web hosting
Introduction to Web hosting

Introduction to Web hosting

Introduction to Web hosting

Introduction to Web hosting

2025-07-21T20:11:20.099975 | Web hosting


So, you want to launch a website? Fantastic! But before you can share your brilliance with the world, you need a place to host it. Web hosting is essentially renting space on a powerful computer (a server) connected to the internet, where your website's files live. This guide will demystify the world of web hosting, covering everything from the basic types to crucial security considerations and the powerful role Linux plays. Whether you're a complete beginner or a seasoned developer, we'll help you understand the ins and outs of choosing the right web hosting solution for your needs. Let's dive in!
Web Hosting Explained: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners and Experts
What is Web Hosting? The Foundation of Your Online Presence
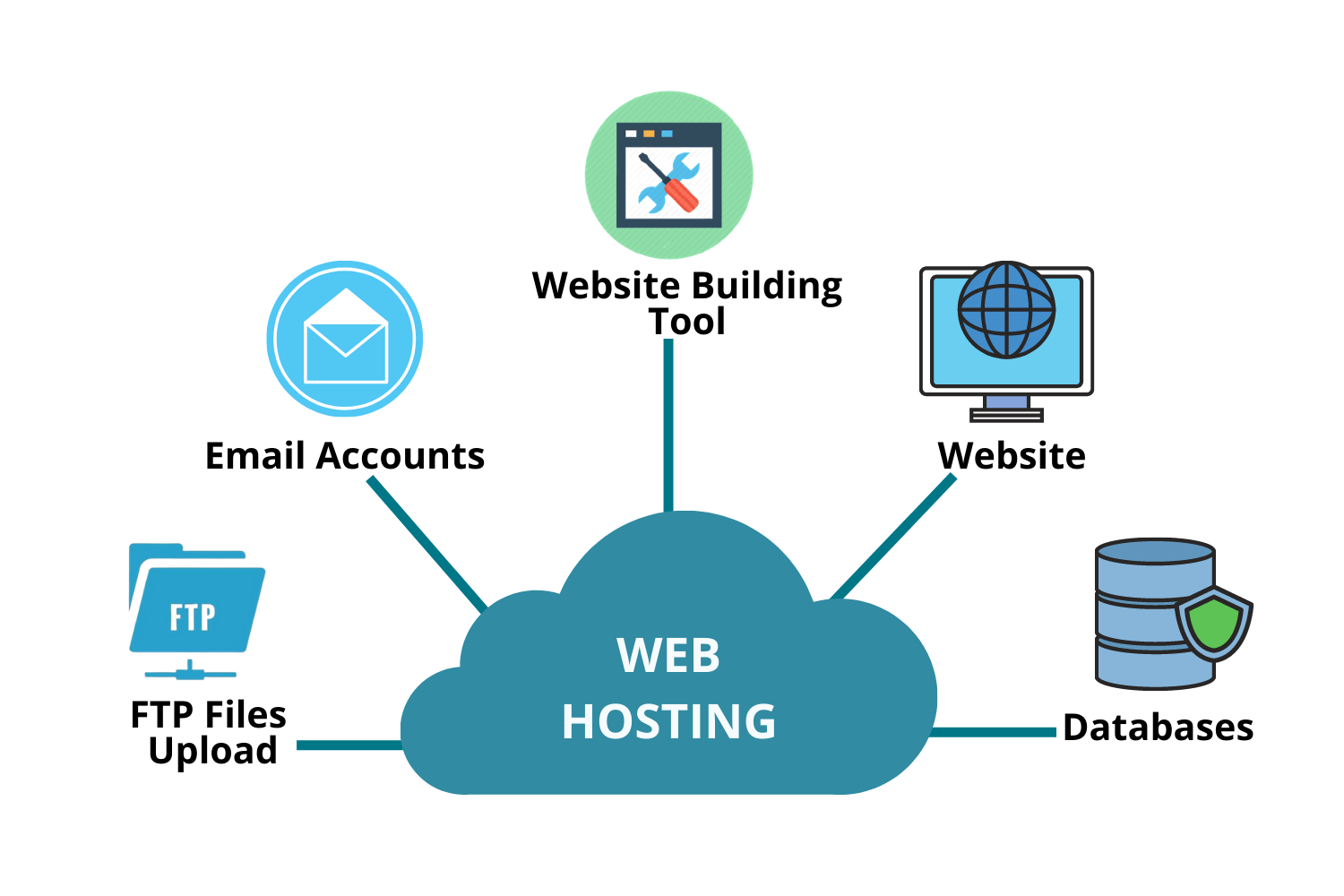
At its core, web hosting is the service that allows your website to be accessible on the internet. Think of it as renting a piece of real estate on the internet. Just like a physical store needs a building and a location, a website needs a server and an internet connection. When someone types your website's address (domain name) into their browser, their computer sends a request to the server where your website is hosted. The server then sends back the files that make up your website, and the browser displays them to the user. Without web hosting, your website would simply be a collection of files sitting on your local computer, inaccessible to anyone else.
Web hosting companies maintain these servers, ensuring they are running smoothly, securely, and connected to the internet 24/7. They also provide the necessary infrastructure and services, such as bandwidth, storage space, and technical support, to keep your website up and running reliably.
Types of Web Hosting: Choosing the Right Fit
The world of web hosting offers various options, each catering to different needs and budgets. Understanding the different types is crucial for selecting the best hosting solution for your website.
Shared Hosting: The Entry-Level Option
Shared hosting is the most common and affordable type of web hosting. In this setup, your website shares a server with many other websites. This means you share the server's resources, such as CPU, RAM, and bandwidth, with other users.
Pros:
- Cost-effective: Shared hosting is the cheapest option, making it ideal for beginners or small websites with limited budgets.
- Easy to use: Hosting providers typically handle server maintenance and updates, so you don't need technical expertise.
- User-friendly control panels: Most shared hosting plans come with a control panel like cPanel or Plesk, which makes managing your website easy.
Cons:
- Limited resources: Sharing resources with other websites can lead to slower loading times or performance issues if one website experiences high traffic.
- Security risks: If one website on the server is compromised, it could potentially affect other websites on the same server.
- Limited customization: Shared hosting plans typically have restrictions on the software and configurations you can use.
Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting: More Control and Resources
VPS hosting is a step up from shared hosting. With VPS hosting, your website still shares a physical server with other websites, but the server is partitioned into virtual servers, each with its own dedicated resources. This gives you more control and resources than shared hosting.
Pros:
- Dedicated resources: You have guaranteed resources, such as CPU, RAM, and storage space, that are not shared with other websites.
- More control: You have more control over the server's operating system and software configurations.
- Better performance: Dedicated resources result in faster loading times and improved performance compared to shared hosting.
Cons:
- More expensive: VPS hosting is more expensive than shared hosting.
- Requires technical expertise: Managing a VPS requires some technical knowledge of server administration.
Dedicated Hosting: Ultimate Performance and Control
Dedicated hosting is the most powerful and expensive type of web hosting. With dedicated hosting, you have an entire server dedicated to your website. This gives you complete control over the server's hardware, software, and configurations.
Pros:
- Maximum performance: Dedicated hosting provides the best possible performance for your website.
- Complete control: You have complete control over the server's operating system, software, and configurations.
- Enhanced security: You are not sharing resources with other websites, which reduces the risk of security breaches.
Cons:
- Most expensive: Dedicated hosting is the most expensive type of web hosting.
- Requires extensive technical expertise: Managing a dedicated server requires advanced technical knowledge of server administration.
Cloud Hosting: Scalability and Reliability
Cloud hosting utilizes a network of virtual servers to host your website. Instead of relying on a single physical server, your website's files are distributed across multiple servers in the cloud. This offers excellent scalability and reliability.
Pros:
- Scalability: You can easily scale your resources up or down as needed, paying only for what you use.
- Reliability: If one server fails, your website will automatically be switched to another server in the cloud, ensuring minimal downtime.
- Cost-effective: Cloud hosting can be more cost-effective than dedicated hosting, especially for websites with fluctuating traffic.
Cons:
- Can be complex: Understanding the pricing structure and management tools for cloud hosting can be complex.
- Less control: You may have less control over the underlying infrastructure compared to dedicated hosting.
- Potential security concerns: While cloud providers invest heavily in security, the multi-tenant nature of cloud hosting can raise some security concerns.
Managed vs. Unmanaged Hosting
Regardless of the type of hosting you choose (shared, VPS, dedicated, or cloud), you'll generally have the option of choosing between managed and unmanaged hosting.
Managed Hosting: With managed hosting, the hosting provider takes care of most of the technical aspects of server management, including server setup, security updates, software installations, and troubleshooting. This is a great option for users who don't have the technical skills or time to manage their server themselves. It generally costs more.
Unmanaged Hosting: With unmanaged hosting, you're responsible for managing your server yourself. This gives you more control, but it also requires a higher level of technical expertise. It typically costs less.
The Role of Linux in Web Hosting: A Powerful and Versatile Platform
Linux is an open-source operating system that is widely used in web hosting. In fact, the vast majority of web servers worldwide run on Linux. Its popularity stems from its stability, security, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Why is Linux so popular for web hosting?
- Stability: Linux is known for its stability and reliability, making it ideal for running web servers that need to be up and running 24/7.
- Security: Linux has a strong security track record, thanks to its open-source nature and active community of developers who constantly identify and fix security vulnerabilities.
- Flexibility: Linux can be customized to meet the specific needs of different web hosting environments.
- Cost-effectiveness: Linux is open-source, meaning it's free to use. This reduces the cost of web hosting compared to proprietary operating systems like Windows Server.
- Compatibility: Linux is compatible with a wide range of web hosting technologies, including Apache, Nginx, PHP, MySQL, and Python.
Most shared hosting plans and many VPS and dedicated hosting plans run on Linux. Even if you're not a Linux expert, you can still benefit from its advantages, as the hosting provider typically handles the underlying server administration. If you plan to use specific technologies like ASP.NET, you might need Windows hosting, but for most websites, Linux is the preferred choice.
Web Hosting Security: Protecting Your Website and Data
Security is a crucial aspect of web hosting. Protecting your website and data from cyber threats is essential for maintaining your online reputation and ensuring the privacy of your users. A robust web hosting provider invests in security measures at multiple levels.
Key Security Considerations for Web Hosting:
- Server Security:
- Data Backups:
- Malware Scanning:
- SSL Certificates:
- DDoS Protection:
- Regular Software Updates:
- Strong Passwords:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Website Firewall (WAF):
Your hosting provider should implement robust server security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. They should also have processes in place to quickly respond to security incidents.
Regular data backups are essential for disaster recovery. Your hosting provider should offer automated backup solutions that allow you to easily restore your website in case of data loss or corruption.
Malware scanning helps detect and remove malicious software from your website. Your hosting provider should offer malware scanning services that regularly scan your website for threats.
An SSL certificate encrypts the communication between your website and your users' browsers, protecting sensitive data such as passwords and credit card information. Make sure your hosting provider offers SSL certificates. Look for HTTPS in the URL - the 'S' stands for secure.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm your server with traffic, making your website unavailable. Your hosting provider should offer DDoS protection to mitigate these attacks.
Keeping your website's software, including your content management system (CMS) and plugins, up to date is crucial for security. Software updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities.
Use strong, unique passwords for your web hosting account, CMS admin panel, and database. Avoid using easily guessable passwords, such as your name or birthday.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your web hosting account and CMS admin panel. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter a code from your phone or email in addition to your password.
A website firewall (WAF) helps protect your website from common web attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Some hosting providers offer WAF as part of their hosting package.
Remember, security is a shared responsibility. While your hosting provider plays a crucial role in securing the server infrastructure, you also need to take steps to protect your website and data.
Choosing the Right Web Hosting Provider: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the right web hosting provider is a critical decision that can significantly impact your website's performance, security, and reliability. Consider these factors:
- Identify Your Needs:
- Research Hosting Providers:
- Consider Uptime Guarantee:
- Evaluate Customer Support:
- Check Server Location:
- Review Security Features:
- Understand Pricing and Renewal Policies:
- Look for Scalability Options:
- Consider Control Panel Options:
- Read the Terms of Service:
- Think about backups
What type of website do you have? What are your resource requirements (storage, bandwidth, CPU, RAM)? What level of technical expertise do you have? Answering these questions will help you narrow down your options.
Read reviews and compare different hosting providers. Look for providers with a good reputation for reliability, security, and customer support.
Choose a hosting provider that offers a high uptime guarantee (e.g., 99.9% or higher). Uptime is the percentage of time that your website is accessible to visitors. Lower uptime can cause lost revenue and traffic.
Test the hosting provider's customer support before signing up. Contact them with questions and see how responsive and helpful they are. Look for providers that offer 24/7 support via phone, email, or live chat.
Choose a hosting provider with servers located in a geographic region close to your target audience. This can improve your website's loading speed.
Ensure the hosting provider offers robust security features, such as firewalls, malware scanning, and DDoS protection. Ask about their security protocols and incident response procedures.
Pay close attention to the hosting provider's pricing and renewal policies. Some providers offer low introductory prices but significantly increase the price upon renewal. Be sure to understand the long-term cost.
Choose a hosting provider that offers scalable solutions, such as VPS or cloud hosting, so you can easily upgrade your resources as your website grows.
Most hosting providers offer a control panel, such as cPanel or Plesk, which allows you to manage your website, email accounts, and other settings. Choose a provider that offers a control panel that you are comfortable using.
Carefully read the hosting provider's terms of service before signing up. Make sure you understand their policies regarding acceptable use, data backups, and service level agreements.
The most important thing is to make sure your data is safe. Check out ConnectQuest's website for tips on backups.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Online Journey
Choosing the right web hosting is a fundamental step in establishing a successful online presence. Understanding the different types of hosting, the role of Linux, and the importance of security will empower you to make informed decisions that align with your specific needs and goals.
Whether you're launching a personal blog, a small business website, or a large e-commerce platform, the right web hosting solution will provide the foundation for a reliable, secure, and high-performing online experience. Take the time to research your options, consider your requirements, and choose a hosting provider that you can trust.
Remember to also investigate [[related-post-1]], [[related-post-2]], and [[related-post-3]] for more information.
With the knowledge and insights gained from this guide, you're well-equipped to embark on your online journey with confidence. Good luck!

Related Posts
Latest Posts
Latest Posts

Introduction To Web Hosting
Latest Posts

Introduction To Web Hosting
Latest Posts

Introduction To Web Hosting
Latest Posts



